We build technologies that let NGOs, CSOs, and the private sector reach last-mile communities
Digital-enabled solutions, such as e-commerce, smartphone apps, and internet resources have significant potential to reshape Africa’s economies, drive innovation, and connect communities. Despite the potential of the digital age, our experience with periphery, vulnerable, and poorer populations, highlights that many are excluded from the benefits of existing digital solutions.
Barriers for last-mile populations to reach existing digital solutions
Key Insight
Sauti’s experience with rural women-led MSMEs found that three-quarters of women traders had achieved, at most, a secondary school education (27% had primary only, and 10% had no formal education). Further, women entrepreneurs typically had poor access to ICT-focused learning experiences and few women can afford the time and lost profits to attend training opportunities during work hours. Further, domestic commitments prevent women from attending workshops in the early morning or evening.
Problem Statement
Comparatively low education and few learning experiences challenge marginalized groups’ perceived benefits to adopting ICTs. The result is that, those with the technological capacity, but lacking the necessary digital literacy, often struggle to navigate online browsers or smartphone apps.
Key Insight
For micro and small-scale women-led businesses, few have access to internet-enabled computers or smartphones. Sauti’s Smartphone Adoption Among Traders surveys of approximately 5,000 traders in Kenya and Uganda’s agricultural sector found that approximately 17% had access to a smartphone with internet access.
Problem Statement
While last-mile populations may have access to basic feature phones, they often face vast digital divides owing to the limits in technological capacity to access digital resources – which often require internet-enabled smartphones
Key Insight
Sauti’s needs assessments among rural traders and farmers found that these last-mile populations spend up to USD $13 per week on internet and airtime costs to access digital resources to support their businesses.
Problem Statement
The costs of internet for poorer populations means that they often economize search and information costs, often by reducing their online consumption of digital information. Combined with bloated digital resources (e.g. large smartphone apps, superfluous online graphics), poorer populations often restrict their use of costly online resources.
Key Insight
Interviews with MSMEs and East African women entrepreneurs highlighted that, even when they could access digital resources, they found that digital resources often did not apply to them. Small-scale informal cross-border traders for instance highlighted that online resources were relevant to larger-scale business operations and not relevant to their business activities.
Problem Statement
Poor technical literacy and overly complicated non-localized language, means that last-mile populations can struggle to adopt the information from digital resources. Further, current digital resources often target contexts that are unfamiliar to last-mile populations.
Tailored Information Platforms for "Low-technology" Environments
Sauti designs robust and purpose-built information platforms to improve the incomes, productivity, and resilience of marginalised communities. Our solutions provide a bridge to online information and leverage local familiarities and capabilities with the following technologies:
 USSD
USSD
- Inclusive Device Compatibility: USSD works on all mobile phones, including basic feature phones.
- Instant Interaction: Real-time communication for dynamic exchanges of real-time information.
- Offline Capability: No internet connection required, ideal for low-connectivity areas.
- User-Friendly and Local Familiarity: Widely used text-based menus (e.g. Mpesa) for easy navigation.
- Cost-Effective: Affordable sessions compared to data-intensive services.
 SMS
SMS
- Widespread Reach: SMS reaches all mobile phones, including basic feature phones.
- Offline Delivery: Messages are stored and delivered when the device is available.
- Low Cost: Economical compared to data-based messaging services.
- Simple Format: Concise text format for clear and straightforward communication.
 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
- Global Presence: WhatsApp is a widely used messaging platform worldwide.
- Rich Media Sharing: Supports various media formats, including images, videos, and documents.
- Real-Time Interaction: Enables instant two-way communication.
- Low Cost: Economical compared to data-based messaging services.
- Longer Character Limits: Allows more information, with more technical detail to be delivered instantly.
Use case example
Sauti’s East African Trade and Market Information Platforms
Sauti’s innovation leverages the competitive advantages of mobile technology in East Africa to deliver tailored trade and market information services to traders and farmers at scale and at a lower end-user cost compared to traditional avenues.
We’ve deployed a mobile-based information platform, accessible on any type of phone by SMS and USSD, through which users can access local, up-to-date, and verified information that is commonly available to internet-enabled populations, but which users without smartphones or internet typically struggle to access.
To-date we’ve had 139,000 users across Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, and Tanzania.
HUMAN CENTERED DESIGN & DATA-DRIVEN INNOVATION
User-Centric Interfaces
We design our services with a deep understanding of users’ needs, preferences, and limitations. This enhances user experience, making information more accessible and user-friendly, resulting in increased engagement.
PROJECT EXAMPLE: Information Platforms Needs Assessment: Kenya’s Women in Trade
Data-Driven Decision Making
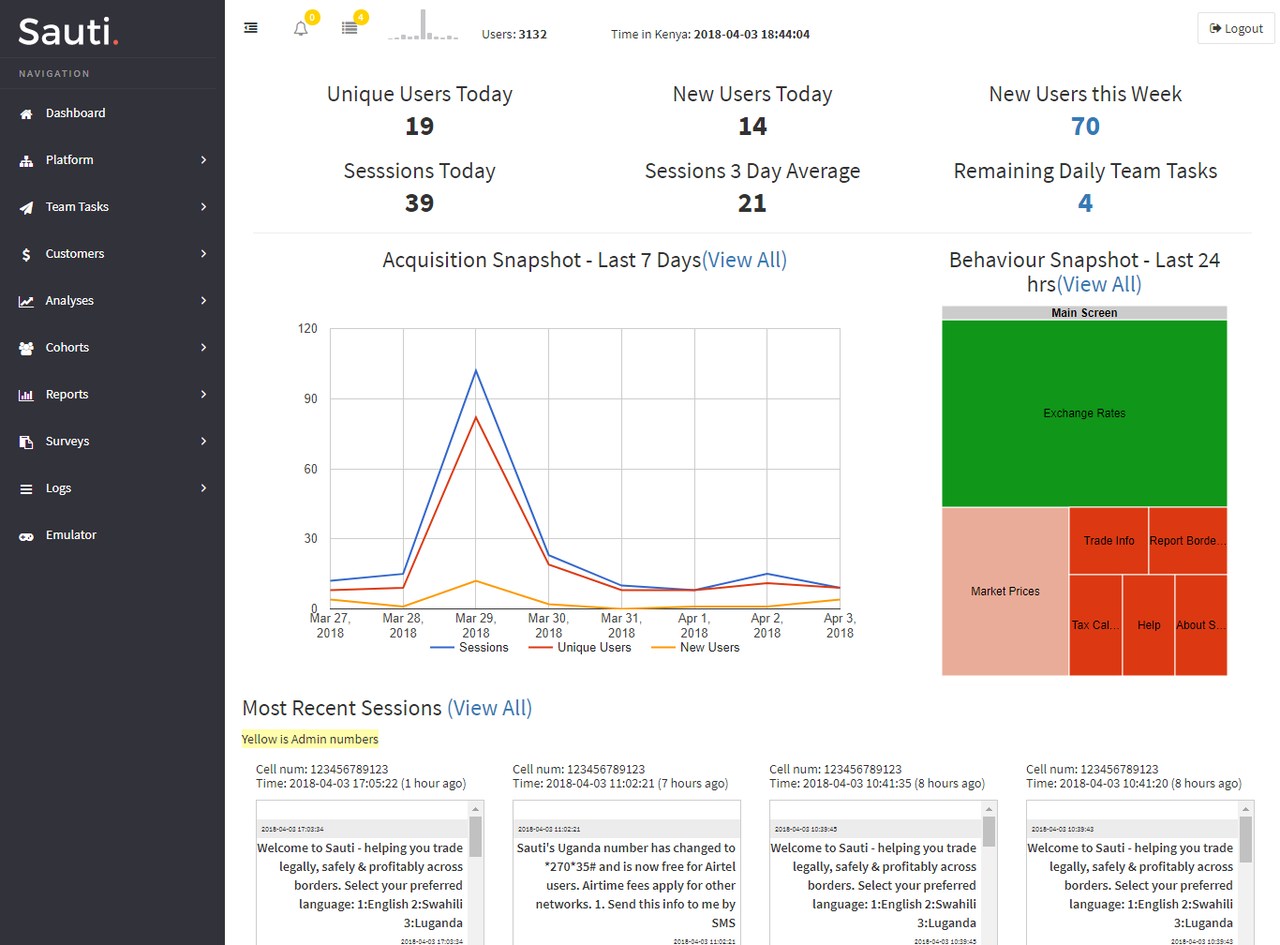
We give solution designers access to real-time data analytics and user feedback to inform service enhancements and content updates. This ensures that platform content provided remains relevant and responsive to evolving user requirements, and fosters continuous improvement.
PROJECT EXAMPLE: Market Monitoring and Predictive Modelling Information Platform
Community Engagement and Co-Creation
We involves communities in the design process, and encourage participation and co-creation of content. This builds a sense of ownership and relevance among users, leading to increased trust, adoption, and sustainability of the service within the community.
Our solutions enable a proactive, data-driven approach to promoting innovation adoption, results measurement, and programme planning.
- Track innovation adoption by integrating real-time usage data into monitoring, evaluation, and learning (MEL) plans and frameworks.
- Adapt programme decisions to maximize adoption and return on innovation investments.
- Understand needs and preferences across stakeholder segments based on usage data.



